"*" indicates required fields
Choosing the right material for your next project is a pivotal decision that can affect not just the performance of the final product but also its cost and longevity. In the ongoing debate between steel and aluminum, industry experts often emphasize the importance of understanding the distinct advantages and limitations of each metal. John Stevens, a renowned materials engineer with over two decades of experience in the steel and aluminum sectors, stated, "The choice between steel and aluminum is not just a matter of strength; it’s about finding the best fit for your project needs."
Both steel and aluminum offer unique benefits: steel is known for its strength and durability, making it an ideal choice for heavy-duty applications, while aluminum’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it suitable for projects where weight is crucial. This nuanced decision-making process requires a careful evaluation of the specific requirements of your project, including load-bearing capacities, environmental factors, and desired aesthetics.
In this guide, we will delve into the key considerations when deciding between steel and aluminum, drawing on expert insights and real-world applications to help you make an informed choice for your next venture. Whether you are constructing a building, designing a piece of machinery, or developing an innovative product, understanding the contrasting characteristics of steel and aluminum is essential for achieving optimal results.

When choosing between steel and aluminum for your next project, it's essential to understand the distinct properties of each material. Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it a prime choice for structural applications. Its resistance to deformation under heavy loads ensures that it can withstand a variety of conditions. On the downside, steel is heavier and more susceptible to rust and corrosion unless treated properly, which can increase maintenance costs over time.
In contrast, aluminum is considerably lighter than steel, which can significantly reduce transportation and handling costs. Its natural resistance to corrosion, due to the formation of a protective oxide layer, makes aluminum an excellent option for outdoor or marine applications. However, aluminum generally falls short when it comes to tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its usage in heavy-duty projects.
**Tips**:
1. Think about the weight requirements of your project. If minimizing weight is crucial, aluminum could be your best option.
2. Consider the environmental factors. If your project will face exposure to moisture or corrosive elements, aluminum's resistance can save you money in the long run.
3. Evaluate the load-bearing needs. For high-stress applications, steel's superior strength may be necessary despite its heavier weight.
When deciding between steel and aluminum for your next project, it’s crucial to evaluate the specific requirements and use cases to make an informed choice. Steel is renowned for its strength and durability, making it an ideal material for heavy-duty applications such as structural supports and industrial machinery. In contrast, aluminum offers a lightweight alternative that excels in applications where weight is a critical factor, like in the aerospace and automotive industries. Understanding the unique demands of your project is essential in guiding this decision.
Tips: Always consider the environmental impact of your material choice. Aluminum is more recyclable compared to steel, which can be an important factor in sustainable construction practices. Additionally, if your project requires resistance to corrosion, aluminum might be favorable due to its natural oxide layer that protects against rust.
Another key aspect is the cost-effectiveness based on project scope and budget. While steel may be less expensive initially, its heavier weight could lead to higher transportation and handling costs. On the other hand, aluminum’s ease of installation can save time and labor costs. Thus, analyzing both short-term and long-term expenses is vital to finding the most suitable material for your specific application.

When selecting materials for construction projects, cost is often a primary consideration, particularly when comparing steel and aluminum. According to the Association of American Steel Construction (AISC), the average price of steel can range from $500 to $800 per ton, depending on market fluctuations. In contrast, aluminum typically comes in at a higher cost, averaging between $1,800 and $2,200 per ton, as reported by the Aluminum Association. This significant difference can influence budget decisions significantly, especially for large-scale projects where weight and material quantities translate into substantial overall costs.
However, the initial material price isn’t the only factor to consider. Life cycle costs, including maintenance and longevity, play a critical role in the decision-making process. Steel, while cheaper initially, may require more maintenance over time due to its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in harsh environments. The Steel Market Development Institute indicates that coating and treatment of steel can add 10-30% to the overall lifecycle costs. Conversely, aluminum’s resistance to corrosion tends to require less ongoing maintenance, prolonging its lifespan and potentially offsetting its initial higher price. A comprehensive economic analysis, therefore, should include not just the purchase price, but also the total cost of ownership over the project's lifespan, making the choice more nuanced than it might appear at first glance.
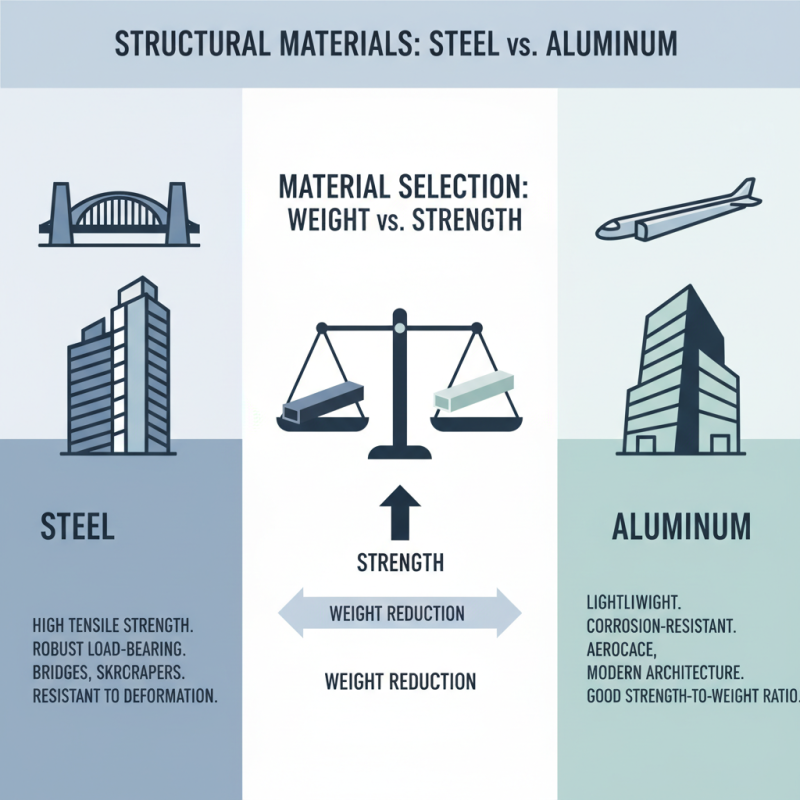
When selecting materials for structural applications, understanding the weight and strength characteristics of steel and aluminum is crucial. Steel, known for its high tensile strength, offers significant load-bearing capabilities. This makes it an ideal choice for projects that require robust structural integrity, such as bridges and high-rise buildings. Furthermore, steel's yield strength and resistance to deformation under heavy loads provide added safety and reliability in construction.
On the other hand, aluminum is renowned for its lightweight nature, making it a favorable option for projects that prioritize mobility and ease of installation. While its strength-to-weight ratio can be impressive, aluminum generally does not match the sheer strength of steel. However, advancements in alloy technology have enhanced the mechanical properties of aluminum, making it suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Ultimately, the choice between these two metals should consider the specific demands of the project, balancing the need for strength with the advantages of reduced weight.
When selecting materials for a project, the environmental impact and sustainability of steel and aluminum play a crucial role. Both metals possess unique characteristics that can influence their ecological footprint. Aluminum, for instance, is known for its lightweight nature and high recyclability. It can be recycled indefinitely without losing its properties, making it an attractive option for projects that prioritize resource conservation. Additionally, the energy required for aluminum production can be mitigated through the use of recycled content, drastically reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin material extraction.
On the other hand, steel, while heavier and generally requiring more energy for production, has its advantages in terms of durability and longevity. Steel structures often outlast those made from aluminum, which can lead to a reduced need for replacements over time. Moreover, advancements in steel production have resulted in more sustainable practices, such as utilizing electric arc furnaces, which can lower carbon emissions significantly. Choosing steel for certain applications can also contribute to a circular economy, as it's one of the most recycled materials globally, with a vast recycling infrastructure already in place.
Ultimately, the decision between steel and aluminum involves analyzing not just the immediate sustainability factors but also the long-term environmental implications of each material within the context of the specific project requirements.






"*" indicates required fields